Invited Expert Discussion - "LAMBDA: A Large Model Based Data Agent"
Introduction: Revolutionizing Data Analysis with AI Agents 🚀
To address the high technical barriers and tedious debugging processes inherent in data analysis, a research team from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University has developed and open-sourced LAMBDA (LArge Model Based Data Agent). LAMBDA employs a dual-agent architecture (“Programmer” and “Inspector”) to enable natural language-driven data analysis. The system supports human-in-the-loop intervention and custom knowledge integration, aiming to reconstruct the interaction paradigm in scientific research and data science education.
Maojun Sun, Ruijian Han, Binyan Jiang, Houduo Qi, Defeng Sun, Yancheng Yuan, Jian Huang.
Lambda: A large model based data agent.
Journal of the American Statistical Association (2025).
Bridging the Gap Between Statistical Logic and Code Implementation
Despite the rise of AI, a significant gap remains between “knowing what to analyze” and “writing the code to do it”. For many researchers, students, and domain experts, complex data cleaning and iterative model debugging consume disproportionate amounts of time.
LAMBDA is designed not to replace human reasoning, but to serve as an intelligent interface. It allows users to focus on hypotheses and analytical logic, while the AI agents handle the translation into executable code and the resolution of runtime errors.
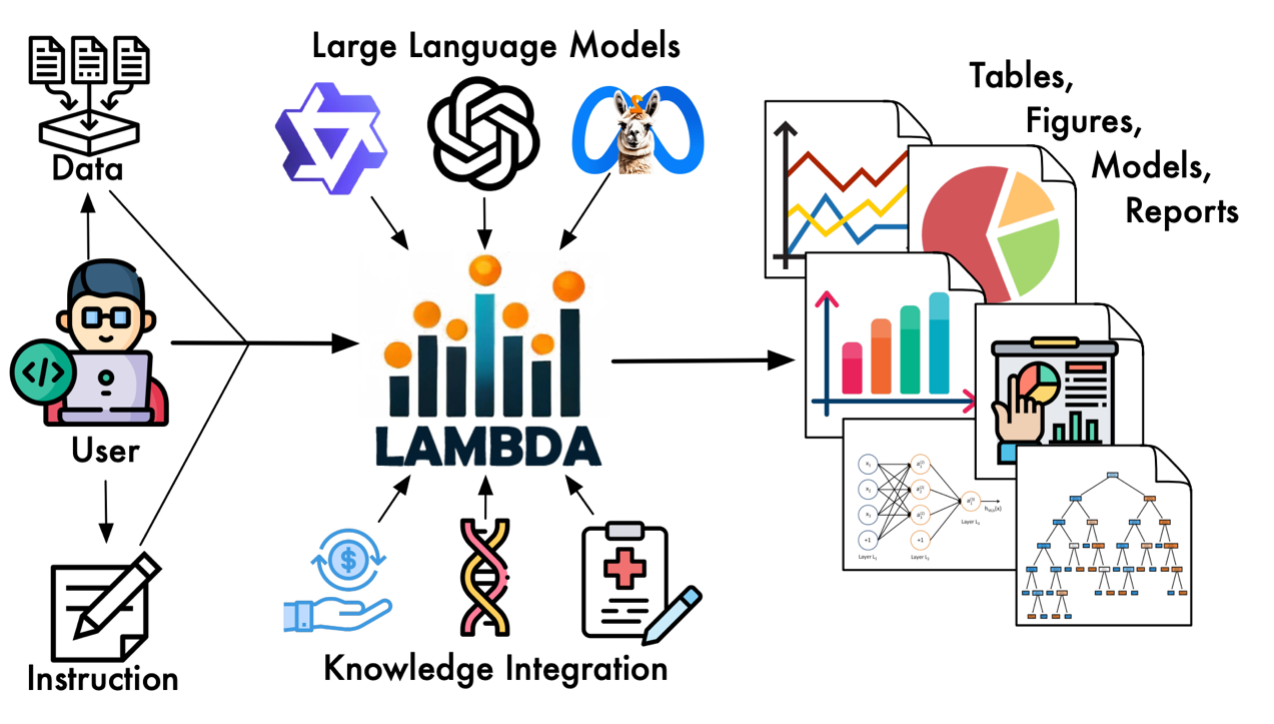
Figure 1: LAMBDA System Overview
System Architecture: Dual-Agent Collaboration with Self-Correction 🤖
Unlike simple “prompt-to-code” tools, LAMBDA utilizes a robust Dual-Agent Collaboration Mechanism:
- The Programmer Agent: Interprets user instructions, analyzes data characteristics, and generates the initial analysis code.
- The Inspector Agent: Monitors execution. Upon encountering errors, it analyzes the traceback, generates specific modification suggestions, and guides the Programmer to iteratively refine the code until execution is successful.
This process mimics human debugging workflows, ensuring high success rates in complex tasks while allowing users to view and intervene in the code at any stage.
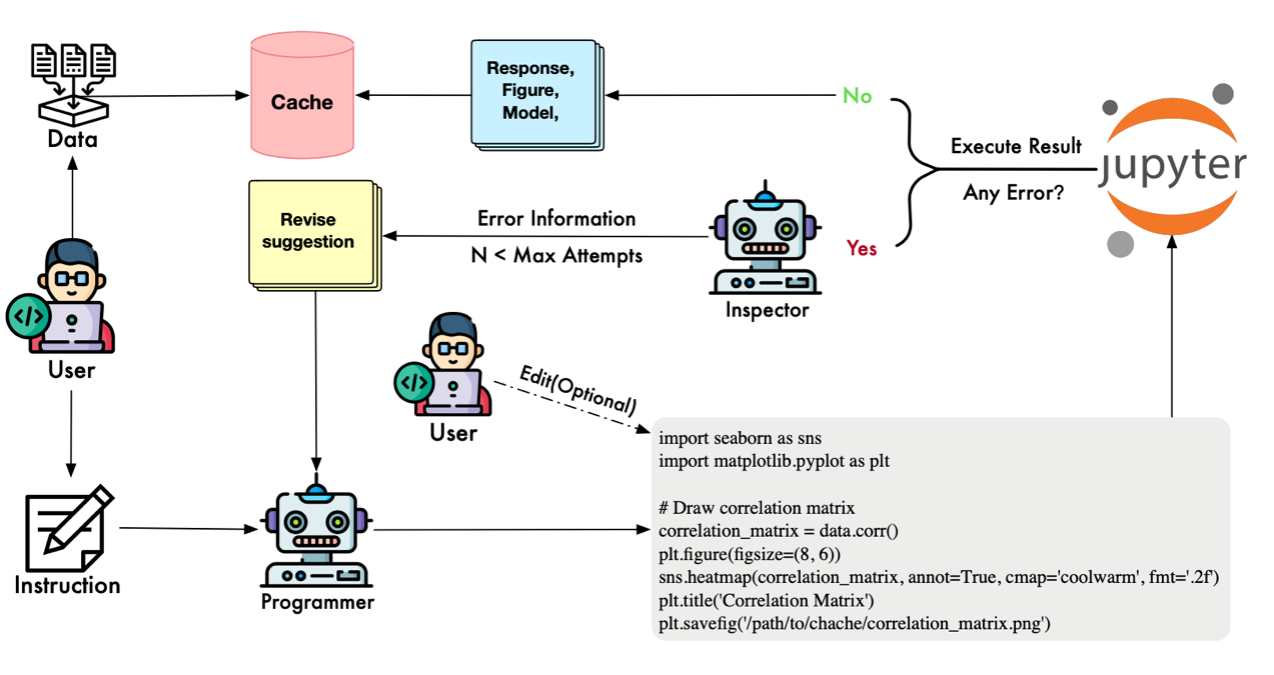
The Knowledge Integration Mechanism 🧠
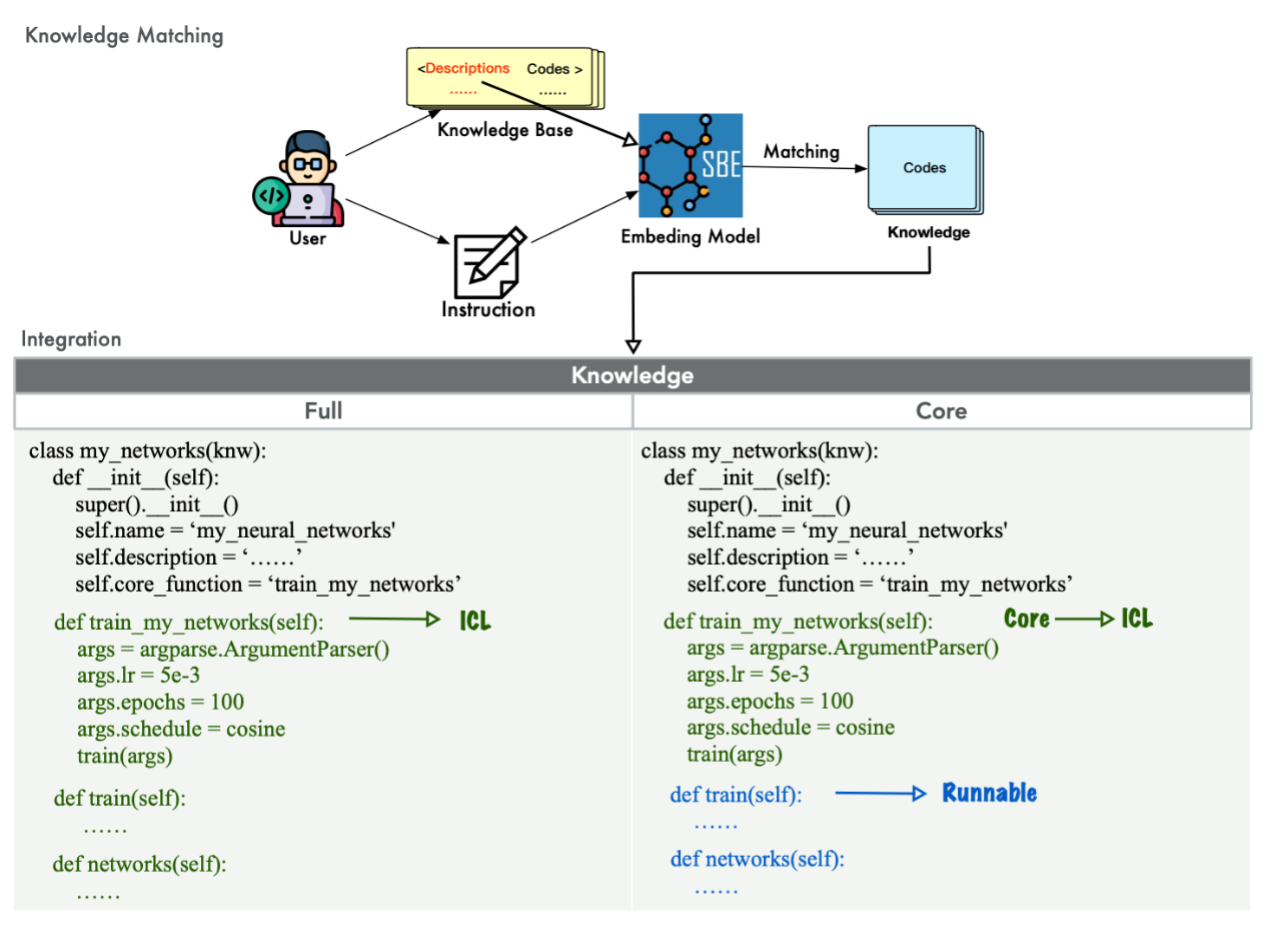
A major challenge for general LLMs is accurately invoking specialized domain algorithms. LAMBDA addresses this via a Knowledge Integration Mechanism. Users can encapsulate custom models and algorithms as key-value pairs within a knowledge base. The system supports two integration modes:
- Full Mode: Injects complete code into the context for comprehensive model understanding.
- Core Mode: Injects only function descriptions while executing complex logic on the backend, preventing context overflow.
This allows LAMBDA to align generated code with specific user intents (e.g., correcting loss function discrepancies) more effectively than standard plugin-based systems.
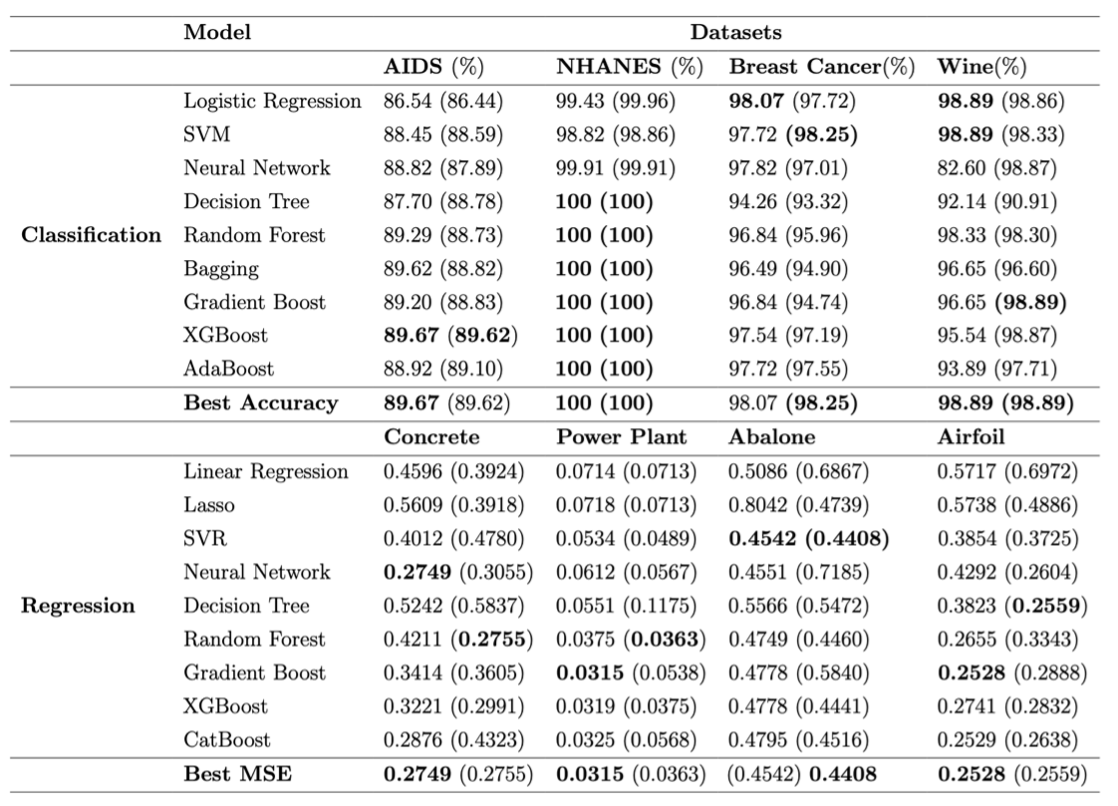
Versatility and Performance
📊 Tabular Data
Achieves modeling performance comparable to human experts in classification and regression tasks.
🖼️ Unstructured Data
Automated invocation of CNNs and Transformers for image classification (e.g., MNIST) and text analysis.
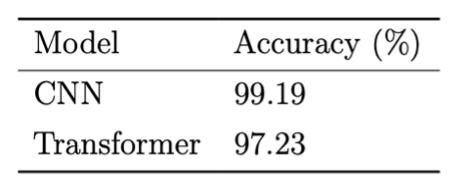

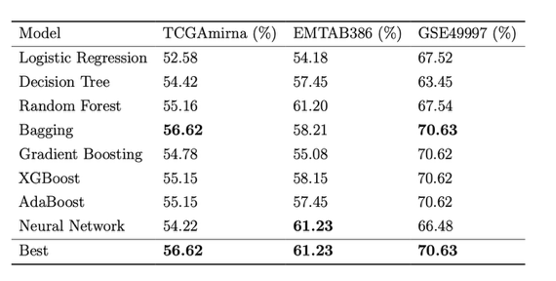
🧬 Complex Scenarios
Effective handling of high-dimensional genomic data and missing value imputation.

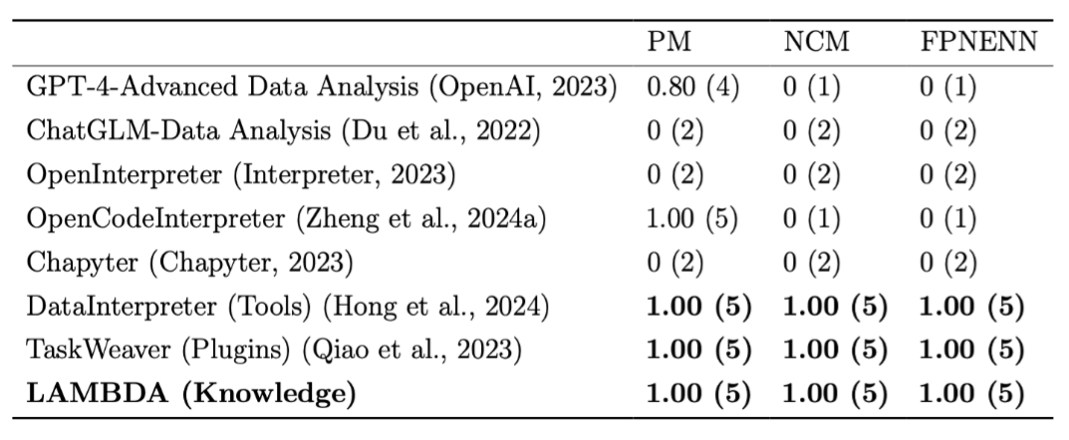
🔧 Knowledge Integration
LAMBDA can actively correct the code of the knowledge base to align with human intent, which is difficult for existing plugin-based agent systems to achieve.

Value in Education and Research
LAMBDA transforms “code” from a barrier into a transparent utility. It supports the export of complete analysis reports and .ipynb files, making it an ideal tool for reproducible research.
In educational settings, it allows students to focus on statistical concepts and problem-solving logic rather than syntax errors, fostering a “Problem-Modeling-Explanation” learning approach.

Discussions: Perspectives and Future Directions
We invited several prominent scholars in statistics and data science to provide comments and engage in a brainstorming discussion. Their perspectives are summarized below.
Professor Donoho describes the release of LAMBDA as arriving at a “pivotal moment” for the discipline. This is an “impressive academic project” that shows how far agentic AI has come in replicating routine data analysis tasks. He suggests establishing rigorous “Chatbot Arena-style” benchmarks specifically designed to evaluate the scientific validity and reproducibility of such agents.
Professor Meng welcomes LAMBDA as a “refreshing article” relevant to “systems thinking” in data science. He appreciates the “Human-in-the-Loop” design, noting that it positions AI as a partner to “build and enhance our mindware”. He proposes the development of a “Data Minder” agent dedicated to data quality and provenance.
They commend LAMBDA for “substantially lowering the barrier to entry” and envision a "Self-Evolving Agent" with long-term memory that can accumulate successful code snippets and problem-solving strategies over time.
Professor Lin lauds the system's practical utility and versatility across diverse datasets (genomic, image, text). She suggests extending the framework with an “Analysis-Planning Agent” to collaborate with users on scientifically valid study designs.
They frame LAMBDA as an “important shift” towards systems capable of handling the scientific workflow. They propose a research agenda focused on Collaborative Agents (like “CollabLLM”) that are explicitly trained to ask clarifying questions when faced with ambiguity.
They value the “Knowledge Integration Mechanism” for enabling domain adaptability. They recommend extending support for the R programming language and refining retrieval mechanisms for complex methodologies like sparse PCA.
Conclusion
LAMBDA represents a foundational step toward intelligent, collaborative data analysis. However, the commentaries suggest its true potential lies not just in automating code, but in evolving into a system that plans, reasons, and teaches—transforming AI from a mere tool into a genuine partner in scientific inquiry.
🌐 Open Source and Collaboration
LAMBDA is now fully open-source. We invite researchers, educators, and developers to explore the system and contribute to its development.